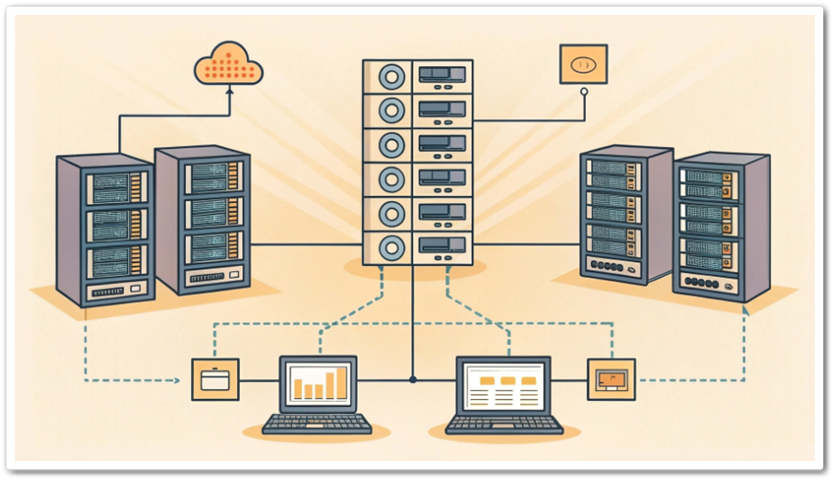
Hierarchical topology, also known as tree topology, is a network structure that organizes devices and connections in multiple layers. This topology efficiently controls data flow, provides scalability, and facilitates easy network management. It is commonly used in distributed processing systems and large-scale networks to maintain an effective communication structure.
Structure of Hierarchical Topology
Hierarchical topology typically consists of the following layers:
-
Core Layer: The topmost layer of the network, responsible for high-speed data transmission and acting as the backbone. It handles large amounts of traffic and supports communication between different layers.
-
Distribution Layer: This layer connects the core layer to the access layer and is responsible for organizing and filtering network traffic. It often includes load balancing and security functions.
-
Access Layer: The lowest layer, directly connecting end devices such as clients and servers. Users or devices access the network through this layer for data transmission.
By structuring networks in this way, hierarchical topology reduces complexity and minimizes the impact of failures in any single layer on the entire system.
Application in Distributed Processing Systems
Hierarchical topology provides several advantages in distributed processing systems:
-
Efficient Resource Management: Each layer performs specific functions, effectively distributing network loads.
-
Scalability: New nodes can be seamlessly integrated into the existing hierarchy, making system expansion easier.
-
Reliability and Fault Tolerance: Failures in a specific layer have minimal impact on the rest of the network, ensuring greater system stability.
-
Enhanced Security: Security policies can be applied at different layers, protecting critical data and reducing potential vulnerabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hierarchical Topology
Advantages
-
Efficient Network Management: Clear role separation across layers optimizes network performance.
-
Flexible Scalability: The network can be easily expanded, making it ideal for corporate environments.
-
High-Speed Data Processing: The core layer, equipped with high-performance hardware, ensures rapid data transmission.
-
Enhanced Security: Access control can be implemented at each layer, improving overall security.
Disadvantages
-
Higher Implementation Costs: More layers require additional infrastructure, increasing setup expenses.
-
Increased Management Complexity: Multiple layers demand additional administrative efforts for configuration and maintenance.
-
Dependence on Centralized Equipment: A failure at the core layer can impact the entire network.
Conclusion
Hierarchical topology plays a crucial role in large-scale networks and distributed processing systems. Its structured design enables efficient network management, scalability, and enhanced security. However, it also introduces higher initial setup costs and management complexity. Therefore, designing an optimal hierarchical topology requires careful planning to align with system requirements. Understanding its characteristics allows organizations to maintain a stable and expandable network infrastructure.
Adaptive ARQ: Maximizing Transmission Efficiency with Dynamic Frame Length Adjustment
2 thoughts on “What is Hierarchical Topology?”